Sepsis
- DefinitionSepsis is a condition that starts with a widespread infection throughout the body and grows into a life threatening condition. In sepsis, the body’s response to the infection creates a new problem: widespread inflammation that can lead to organ failure.
- CausesWhile a great deal is known about the way sepsis injures the body, much remains to be learned. We know that sepsis follows an infection and that certain people are more vulnerable, but why certain people are severely affected and not other remains unclear.
- TreatmentThe most important way to stop sepsis is to prevent infections or treat them early. An international effort is underway to treat sepsis (the Surviving Sepsis Campaign). Identifying patients with sepsis quickly and treating the infection aggressively is essential for success, as is identifying the original source of the infection.
Traumatic Brain Injury
Definition
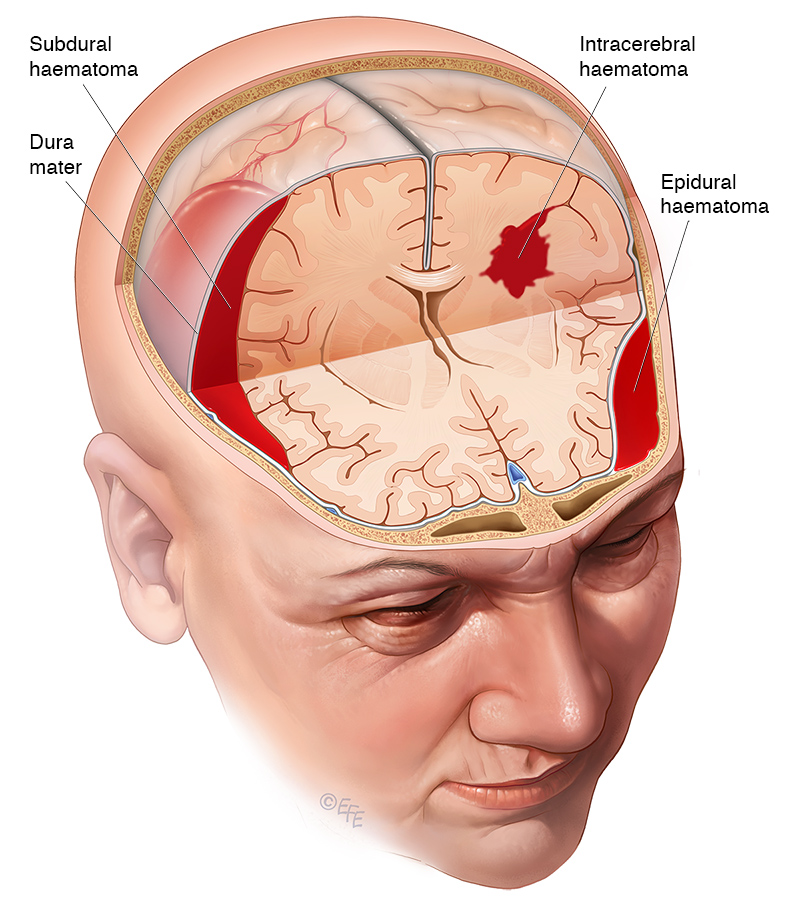
Traumatic brain injury involves temporary or permanent damage to brain tissue. It is usually the result of a hard impact to the head or face and is often associated with bleeding into the brain and/or swelling of the brain. Depending upon the severity of the traumatic brain injury, symptoms may range from confusion, to loss of consciousness, to coma, all of which may vary in duration.
Causes
Common causes of traumatic brain injury are automobile accidents, falls, sporting accidents and industrial accidents.
Treatment
The treatment of traumatic brain injury involves support of all vital body systems. Because the brain often swells following injury, pressure within the skull may increase. Under these circumstances further brain injury may occur and measures to lower pressure within the brain are used.
Severity of traumatic brain injury varies greatly. Some patients recover completely, while others may suffer severe, permanent brain damage or death.
Ruptured Brain Aneurysm
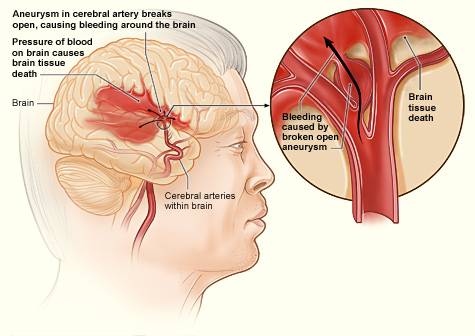
- DefinitionAn aneurysm is a dilation (ballooning) and weakening of the walls of a blood vessel. When an aneurysm in the brain bursts, it causes bleeding into the brain, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
- CausesMany aneurysms are congenital (present since birth). The blood vessel wall may become weakened by age, physical injury to the vessel, or hardening of the arteries.
- TreatmentUsually a brain CT scan is required for diagnosis. Care focuses on treating the cause of the aneurysm and repairing the blood vessel. This often means controlling the blood pressure to prevent stress on the aneurysm, followed by surgery to repair the vessel. If the vessel bursts, care focuses on preventing further bleeding.
Shock
- DefinitionShock is the slowing of blood flow to the vital organs (brain, lungs, heart, kidneys and others). Shock occurs when blood pressure and flow are not strong enough to supply blood to to the vital organs.
- CausesThere are many forms and causes of shock. The most common ones are a weak heart, bleeding or a severe infection.
- TreatmentTreatment depends on the cause of shock but usually is aimed at restoring blood pressure and blood flow to vital organs.
Stroke
Definition
An aneurysm is a dilation (ballooning) and weakening of the walls of a blood vessel. When an aneurysm in the brain bursts, it causes bleeding into the brain, known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
Causes
Many aneurysms are congenital (present since birth). The blood vessel wall may become weakened by age, physical injury to the vessel, or hardening of the arteries.
Treatment
Usually a brain CT scan is considered by the specialist doctor for the diagnosis. Care focuses on treating the cause of the aneurysm and repairing the blood vessel. This often means controlling the blood pressure to prevent stress on the aneurysm, followed by surgery to repair the vessel. If the vessel bursts, care focuses on preventing further bleeding.
Trauma
- DefinitionTrauma can take many forms: most trauma is cause by motor vehicle accidents or falls. Less commonly people may be the victim of an assault which may involve blunt objects, stabbing, or shooting.
- CausesTrauma may result in an assortment of injuries to various parts of the body. Trauma to the head may result in a traumatic brain injury. Trauma to the neck or back may result in spinal cord injury and paralysis. Trauma can also involve the organs of the chest or abdomen, as well as broken bones.
- TreatmentThe specific treatment required will depend on the part of the body that is injured. Some traumatized patients require surgery to repair damage or stop bleeding, others require specialized medical treatments.
Post-operative Intensive Care
- DefinitionSome patients may require monitoring in the ICU after surgery. Sometimes this is planned, as in after major vascular or cardiac surgery. In other cases the ICU admission is not planned ahead of time but becomes necessary after a problem occurs during the surgery.
- CausesThere are several problems which may occur during surgery which may lead a patient to the ICU. Common examples include unexpected bleeding, low blood pressure, problems with heart rhythm, or difficulty with breathing.
- TreatmentPatients whose admission to ICU was planned in advance typically require a short period of monitoring in ICU before being transferred out. For patients admitted unexpectedly, the treatment required will depend on the nature of the problem.
Heart Failure
Definition
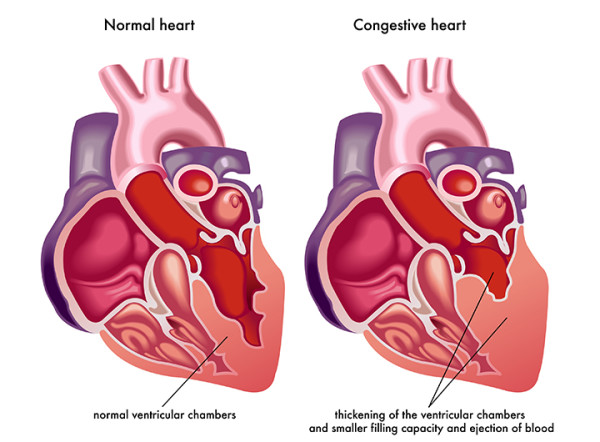
There are a variety of emergencies related to the heart which can lead a patient to require admission to the ICU under the observation of a heart specialist doctor. Many of these patients will be admitted to the Coronary Care Unit (CCU) or the Cardiac Surgery ICU (CSICU), but some are best cared for in the ICU. The most common heart problem leading to ICU admission is heart failure.
Causes
Heart failure is a situation where the pumping muscles of the heart become too weak to circulate enough blood around the body. Shock and organ failure may occur.
Treatment
The treatment for heart failure depends on it’s cause. Patients with blockages in the arteries of the heart or problems with the heart valves may require surgery or the placement of stents. Most patients are treated by heart specialist with medications which improve the heart’s pump strength and help to increase blood flow around the body.
Cancer-related Intensive Care
- DefinitionPatients with cancer sometimes require admission to the ICU. While this can happen for a number of reasons, frequently it occurs after chemotherapy or a bone marrow transplant because of bleeding or infection.
- CausesPatients with cancer often have weakened immune systems, especially those who have recently received chemotherapy or a bone marrow transplant. This can make them more prone to infections, some of which may become life-threatening. They can also be prone to bleeding due to low levels of platelets, the cells responsible for helping blood to clot.
- TreatmentThe treatments required will depend on the specific problem which leads the patient to need ICU under the observation of a cancer specialist doctor. Patients with infection are usually treated with antibiotics, and patients with bleeding may require transfusions of red blood cells or platelets.
Acute Respiratory (Lung) Failure
- DefinitionThe purpose of the lungs is to bring oxygen into the bloodstream and remove carbon dioxide. When these basic functions are impaired, a life-threatening situation may occur.
- CausesThere are many causes of respiratory failure, but the most common cause leading to ICU admission is lung infection (pneumonia). Pneumonia can be caused by infection with bacteria, viruses, or a fungus. Severe pneumonia can result in severe inflammation of the lungs, a condition called the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), which can be very dangerous.
- TreatmentPneumonias are usually treated by the lung specialist doctors with combination of antibiotics and supportive care. Patients with severe pneumonia often require mechanical ventilation (a “respirator”) to support their breathing until their lungs improve.